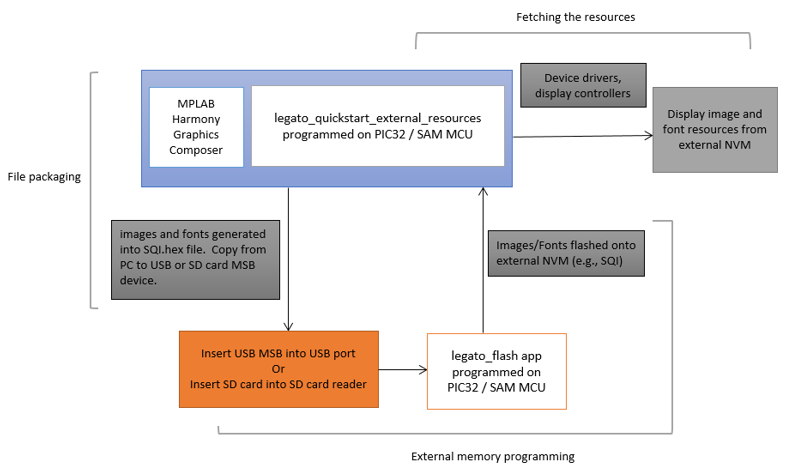
Applications requiring multiple images or non-alphabet-based languages with large number of glyphs, have a very large NVM requirement for their graphics resources. In such applications, storing these graphics resources on-chip may be inefficient or impossible. The solution is to store the graphics resources to off-chip NVM, thereby preserving the on-chip NVM for program memory and allowing for more complex functional features.
The legato_quickstart_external_resources (external flash reader) application populates some of its user interface from assets stored on on-chip NVM and other parts of it from assets stored as binary data on an external NVM. The resources are previous copied into the external NVM using the legato_flash application.
To demonstrate how to access graphics resources stored on an external memory device, three components are needed:
• File Packaging
• Bootloader Application
• Fetch Application
The following figure shows the external resources process diagram.
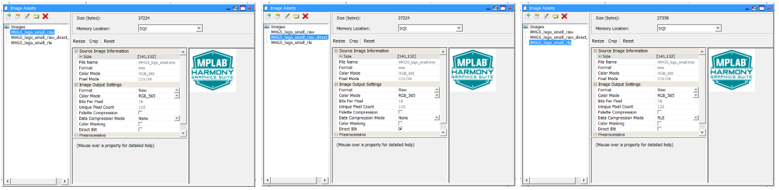
The same image, stored externally as three different encoding formats, are demonstrated: Uncompressed RAW, Run-Length Encoded (RLE), Palette Compressed images.
The legato_quickstart_external_resources (external flash reader) application also demonstrates the ability of the Legato Graphics Library to support multiple languages in the same application build. One language is alphabetic (English) and the other is non-alphabetic (Chinese). English is supported via the Basic Latin Unicode Range (ASCII 32 to 127).
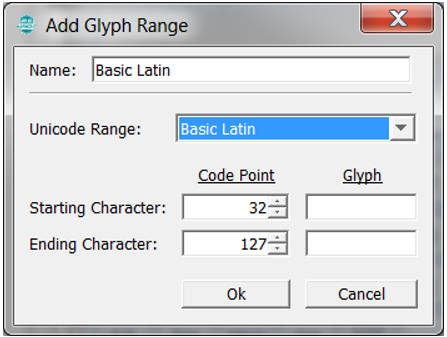
For Chinese, the MPLAB Harmony Graphics Composer’s built-in automatic glyph filter is overridden to use the enter CJK Unified Ideographs Extension 1 (UTC 32,968 to 40,959). This covers the most used kanji glyphs. The glyphs for both languages are generated as binary data, programmed into external NVM, retrieved and displayed from external memory at runtime.

|
MPLAB® Harmony Graphics Suite
|