Layer Clipping
In order of the processing, Layer Clipping is first applied to the image. If the image extends beyond the edges of the layer that contains it then those pixels are not drawn. Failure to clip out-of-bound pixels can cause the application to crash. The following figures shows an example of layer clipping:
Before applying layer boundaries:

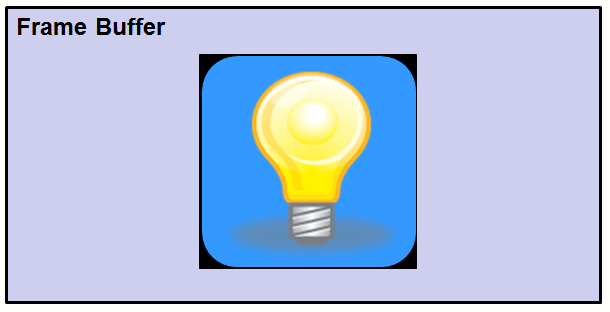
After applying layer boundaries:
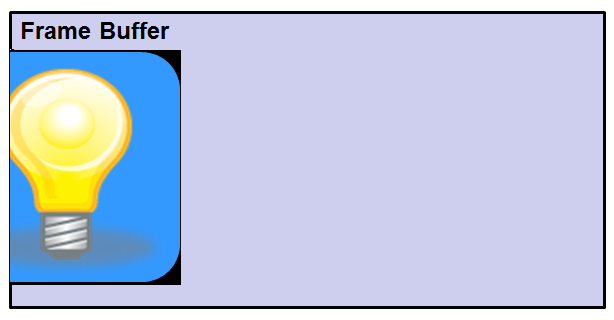
Rectangle Clipping
Next, the image is clipped to the boundaries of any widgets that contain it as a parent, such as a rectangle.
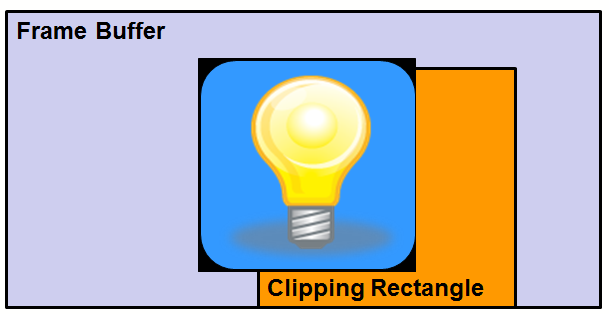
Before applying the clipping rectangle.:
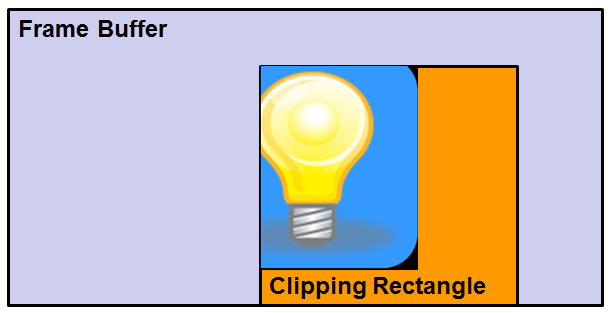
After applying the clipping rectangle:
Color Masking of Pixels
Pixels in the image are matched to a mask color. If the colors match the pixel is discarded (not drawn). In the following example, the black border of the image is removed by defining the mask color to be black.
Before applying color mask:
After applying color mask:

Orientation and Mirroring
The logical orientation of the graphics design may not match the physical layout of the display. Pixels may need to be reoriented from logical to physical space before being rendered.
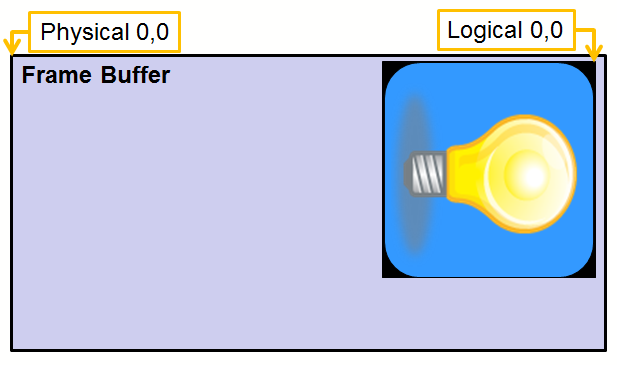
Pixels may also need to be flipped (mirrored) before being rendered.
![]()
Alpha Blending
Each pixel drawn is a composite of the image color and the background color based on the alpha blend value defined by a global alpha value, the pixels alpha value, or both.
Before alpha blending:

After alpha blending:
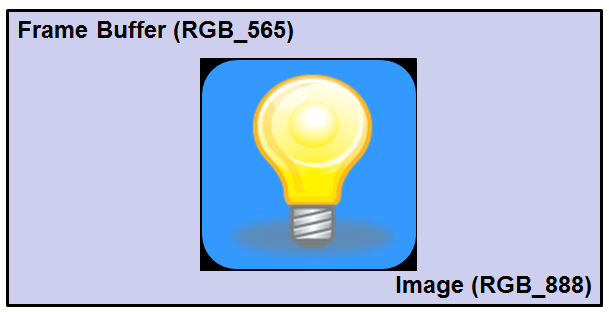
Color Conversion
The image color format may not be the same as the destination frame buffer. Each pixel must be converted before it is written. In the following example, the image is stored using 24 bits per pixel; however, the frame buffer uses 16 bits per pixel.
Frame Buffer Write
The final stage in rendering an image is to write each-color converted pixel to the frame buffer.
|
MPLAB® Harmony Graphics Suite
|