Many parts of a graphics design are implemented using memory allocated from the application’s heap space. Therefore, it is important to allocate sufficient memory for the heap. This tool can estimate heap usage by the allocation based on the widgets, layers, screens, and decoders currently in the design.
When launching the tool from the Tools menu, the Heap Configuration window appears.
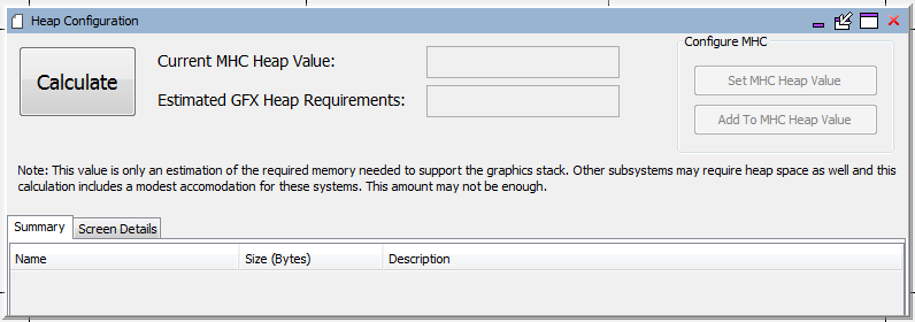
Clicking Calculate estimates heap usage. The following figure shows what occurs within the Aria Quickstart demonstration if the heap space is only 4096 bytes:
The Summary tab shows how the estimated heap requirements was derived by summing up all the sizes shown under the “Size (Bytes)” column. Note that the largest contribution comes from the screen requiring the largest heap allocation (in this case MainMenu).
If there is insufficient memory allocated to the heap, an exclamation point ( ! ) appears in the window. Hovering the mouse pointer over this icon and the following message appears:

The user can click Set MHC Heap Value to reset the heap allocation to match the estimated requirements. Selecting Add to MHC Heap Value adds the estimated heap requirements to the current heap value. (In the case above, this would change the heap allocation to 4096+10664 bytes.)
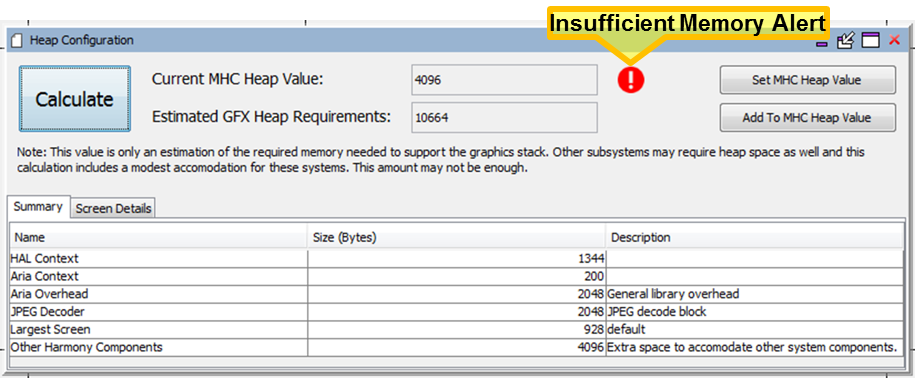
Alternately, the user can set the heap allocation to a larger value by going to MHC's Project Graph panel, clicking on the System component, and then editing the Heap Size shown under the Configuration Options panel:
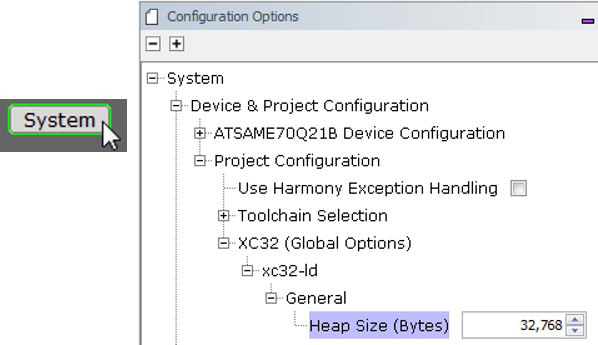
The Screen Details tab (from the Aria Showcase demonstration) shows screen-by-screen the heap space needed for each layer and widget on the screen selected.
|
|
After you have updated the Heap Size, either using the Heap Estimator tool or by directly editing the value as shown above, you must regenerate the project using the Generate Code button. This will update the actual heap size value used in building the application. |
Clicking the “Name” column will alphabetize the list. Clicking the “Size (Bytes)” column sorts the assets by size, with the largest at the top and smallest at the bottom.
This sub-tab can help in managing the application’s utilization of heap space. For example, excess use of cached backgrounds for widgets can become ruinously expensive, expanding the application’s need for heap well beyond the capabilities of the device. As an example, consider a screen label from the Aria Showcase demonstration.
The Heap Estimator tool shows that if caching is enabled for the label’s background, this widget requires 23699 bytes of heap to store the widget. Note that the label is twice the size of the text it contains, so one way of reducing the cost of the widget is to make it smaller, thereby reducing the number of background pixels that must be stored. If the label is resized, the heap allocation is reduced to 11688 bytes, which is a drop of appoximately 50%. Finally, if the background is changed from “Cache” to “Fill” the widget only needs 188 bytes.
The lesson learned is to use Cache as a background only for widgets where it is absolutely necessary and to make the “cached” widgets as small as possible.
|
MPLAB® Harmony Graphics Suite
|