MHGC supports various image formats and the MHGC Image Assets Manager provides the ability to convert and store a source image into to the following formats
- Bitmap RAW
- Bitmap Raw Run-Length Encoded (RLE)
- JPEG
- PNG
- Predecoded RAW Bitmap in DDR (PIC32MZ DA)
The following table shows the relative rendering time and Flash memory requirements of the different image formats in the MPLAB Harmony Graphics Library. The rendering time includes decoding the image and drawing it to the screen. This information is helpful when optimizing a MPLAB Harmony graphics project for performance and Flash memory space. For example, as shown by the red highlighted text in the table, a 40x40 pixel 16-bit RAW image renders 2.38 times faster and uses 2.59 times more Flash space than a JPEG image.
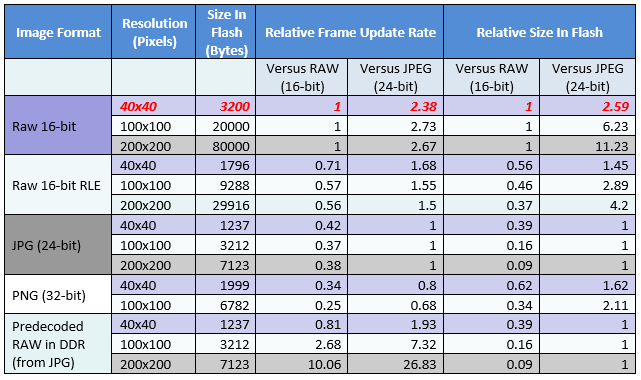
For PIC32MZ DA devices with DDR, the MHGC Image Asset Manager provides an option to predecode images from Flash and store them into DDR as RAW images. The GPU is used to render the decoded image from DDR to the frame buffer. This provides a faster render time than an equivalent RAW image in Flash memory, specifically for large images (up to 10 times faster for a 200x200 image). Conversely, predecoding small images 40x40 pixels or smaller in DDR may not render faster due to the additional overhead of setting up the GPU.
Recommendations:
- If there is adequate DDR memory available, consider predecoding images to DDR for best performance
- Using JPEG images and predecoding them into DDR can provide the best rendering performance and most Flash memory savings.
|
|
The images are decoded from Flash to DDR memory by the Graphics Library during initialization and may introduce delay at boot-up, depending on the number and size of the images. |
RAW images provide fast rendering time, as there is no decoding needed. However, depending on image content, it can be two times larger than a Run-Length Encoded (RLE) image and about 3 to 10 times larger than a JPEG.
Recommendation:
For small images that are to be rendered frequently, consider using a RAW image for better performance
JPEG images provide the most Flash space savings, but are slower to render compared to RAW and RAW RLE.
Recommendations:
- If images are large and not used frequently, consider using the JPEG image format to save flash memory space
- If DDR memory is available, consider predecoding JPEG images in DDR for better rendering performance
In terms of rendering speed and size, RAW RLE images are in between RAW and other compressed formats like JPEG or PNG. Depending on the image contents, RAW RLE can be approximately 1.5 times faster than JPEG, but could be significantly larger in size for large images. Again, depending on the image content, RAW RLE can be about half the size and performance of a RAW image.
Recommendation:
If optimizing your application for both speed and flash size consider using RAW RLE images
Among the image formats, PNG is slowest to render and requires more memory to decode.
Recommendations:
- Unless fine levels of alpha-blending are needed, it is better to use other image formats to achieve the best performance. Use the MHGC Asset Manager to convert the source PNG image and store it in a different image format.
- If you would like to use an image with a transparent background, it may be better to use a RAW RLE image with background color masking to achieve the same effect with better performance than a PNG. Color masking is supported in the MHGC Image Asset Manager.
|
MPLAB® Harmony Graphics Suite
|